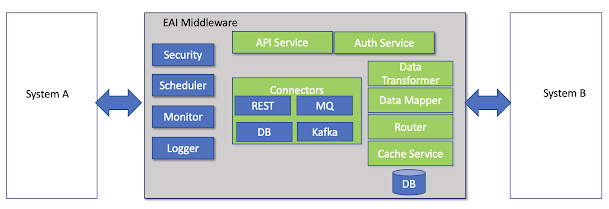
Enterprise architecture strategy mandates systems to measure the quantifiable metrics. There are challenges to this mandate for certain type of applications and environment those applications need to perform. Systems that work in backend with no user interface, systems in CIO which only caters to internal workforce are few examples for that. KPIs related to revenue and UX performance are the most popular ones. There are many other SMART KPIs that helps teams to figure out health of the system. Here SMART is acronym for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Timely metrics. As an example, I'm discussing about Data Sharing Platform in this blog to provoke readers thoughts.
Data Sharing System
- Data Volume
- Data sources: Number of data sources from where data flows in to the platform. This proves the capability of system in connecting to various data sources especially when the sources are heterogeneous.
- Incoming flow rate: Data can flow either in real time or batch mode. The rate in which the data flows in to the platform needs to be measured. For eg: 2 million records per hour
- Outgoing flow rate: Similar to Incoming data flow rate, outgoing flow needs to be collected as well. Various users or external systems where data flows should be logged and collected as matrix.
- Total Volume:The total size of the data in the system on any day
- Real time and Batch jobs : Number of jobs to pull and push data in real time or in batch mode.
- Data Protection
- Data restriction: Restricted data like US federal, DACH should not be accessed by all. The number of such restrictions should be captured for metrics purpose.
- Sensitive data protection: If there is a scenario where data needs to be encrypted or masked irreversibly, it must be measured as well. How many such fields are masked in what all entities is the good metrics for quicker understanding.
- Number of user/group roles: How many types of users/ groups accessing their system and each of their access roles must be recorded and monitored.
- Accessibility
- Time to onboard new data consumers: The time taken to onboard users proves the good usability of the data sharing platform. Discovery, access, and data exploring are crucial for the users and building trust among the collaborators.
- Metadata views: Catalog provides the preface to the data. A good data catalog solves various issues and saves lot of time.
- Total number of consumers: This metrics not only shows the popularity, but also important for capacity planning of the system.
- Data Quality
- Support tickets: The number of bugs/defects reported should be continuously measured. This metrics is directly proportional to the hygienic overview of the system.
- User Queries: The queries/help calls/chat sessions should be measured to monitor the ease of use.
- Build and Maintenance Effort
- Total Team Size
- Updates: The number of updates/upgrades to the system in a given period shows the team effort and helps in sizing and revenue calculation
- Cleanup: The cleanup activities taken up by administrators is another indicator for data quality.
- Infrastructure
- Uptime : The system uptime is critical and shows business
- Cost: Infrastructure cost is easy to collect and required to derive various other business metrics.
- Licenses : Number of thirdparty licenses acquired to build the system, expiry date for each of them.
- Number of Hardware: Number of hardware resources allotted.
- Number of Software/SaaS : Number of software installed or SaaS services provisioned.
- Data Backup: Backup frequency, store format, users having access
- Disaster Recovery: RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) are key metrics in determining database backup and disaster recovery requirements.
- Business KPIs
- ROI: Collection of this key metrics is the ultimatum for every software. This requires deep financial understanding. Infrastructure cost, resources cost, operational cost and etc. needs be collected to derive the ROI.
- NPS: User surveys, questionnaire, campaigns and etc. provides information about this yet another key metrics.